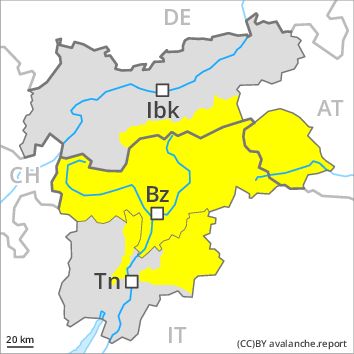
Regions
Sexten Dolomites, Latemar, Val Müstair Alps, Langtaufers, Schnals Ridge, Southern Stubai Alps, Southern Zillertal Alps and High Tauern, Saldurn-Mastaun Ridge, Texel Mountains, Sarntal Alps, Western Pfunderer Mountains, Southern Lagorai, Northern Lagorai, Pine' - Mocheni Valley, Eastern Pfunderer Mountains, Durreck Range, Western Rieserferner Mountains, Western Deferegger Alps, Central Stubai Alps, Ortler Range, Northern Zillertal Alps, Ulten Valley, Venediger Range, Eastern Nonsberger Alps, Eastern Rieserferner Mountains, Northern Dolomites of Fiemme, Glockner Range, Gröden Dolomites, Primiero - Pale di S. Martino, Eastern Deferegger Alps, Prags Dolomites, Schober Mountains, Lienzer Dolomites, Western Nonsberg Alps, Fassa Valley, Paganella
Danger level
Avalanche Problem
Gliding snow above 2600m, E-SE-S-SW-W
Wind-drifted snow above 2400m, N-NE-E-W-NW

Gliding snow represents the main danger. Wind slabs require caution.
The sometimes avalanche-prone wind slabs must be evaluated with care and prudence in particular on west to north to east facing aspects above approximately 2400 m. At high altitudes and in high Alpine regions avalanche prone locations are more prevalent. Caution is to be exercised in particular adjacent to ridgelines. Individual gliding avalanches are possible, even quite large ones, especially in the regions with a lot of snow below approximately 2600 m. Areas with glide cracks are to be avoided as far as possible.
Snowpack
dp 2: gliding snow
dp 6: cold, loose snow and wind
The fresh wind slabs are clearly recognisable to the trained eye. They are mostly rather small but can in some cases be released easily at their margins. The older wind slabs have bonded quite well with the old snowpack. Faceted weak layers exist deep in the old snowpack above approximately 2800 m. The snowpack will become gradually moist, especially on steep sunny slopes below approximately 2000 m.
Tendency
In some localities increase in avalanche danger as a consequence of fresh snow and wind.