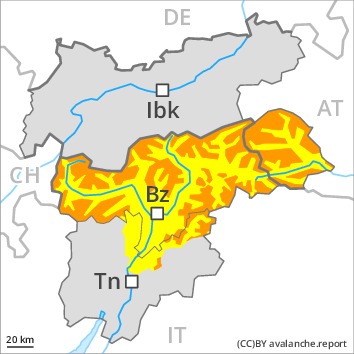
Danger level
 | 2000m
|
Avalanche Problem
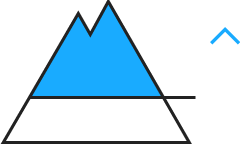
 | | Wind-drifted snow |
|  | |  |
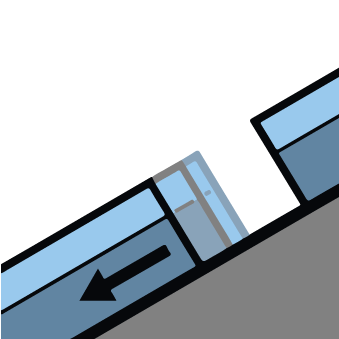 | | Gliding snow |
|  | |  |
 | | Persistent weak layer |
|  | |  |

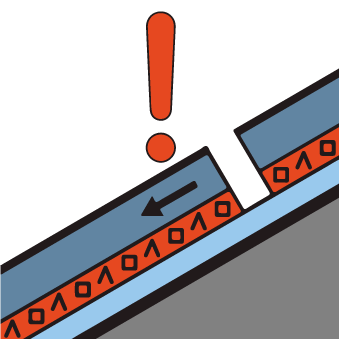
Fresh wind slabs represent the main danger. Gliding snow requires caution.
High altitudes and the high Alpine regions: The fresh snow and in particular the sometimes deep wind slabs can be released easily, or, in isolated cases naturally in all aspects. The number and size of avalanche prone locations will increase with altitude. Avalanches can also penetrate deep layers and reach dangerously large size. Weak layers in the upper part of the snowpack can still be released in some places by individual winter sport participants in particular in areas where the snow cover is rather shallow.
Low and intermediate altitudes: A latent danger of gliding avalanches exists. Areas with glide cracks are to be avoided as far as possible.
Snowpack
dp.6: cold, loose snow and wind
dp.2: gliding snow
The fresh wind slabs are lying on soft layers in all aspects above the tree line.
The old snowpack is moist, in particular at low and intermediate altitudes.
Avalanche prone weak layers exist in the centre of the snowpack in all aspects, in particular above approximately 2000 m.
Tendency
Fresh wind slabs require caution. In addition a latent danger of gliding avalanches exists.
Danger level
 | treeline
|
Avalanche Problem
 | | Wind-drifted snow |
|  | |  |
 | | Gliding snow |
|  | |  |
 | | Persistent weak layer |
|  | |  |

At elevated altitudes a considerable avalanche danger will still be encountered. Fresh wind slabs represent the main danger. Gliding snow requires caution.
The new snow and wind slabs remain very prone to triggering in all aspects above the tree line. This applies in particular on very steep slopes, and adjacent to ridgelines. Dry avalanches can be released by small loads or triggered naturally.
In particular on very steep sunny slopes more small and, in isolated cases, medium-sized slab avalanches are possible. They can also penetrate deep layers and reach quite a large size. In addition a latent danger of gliding avalanches and moist snow slides exists.
Extensive experience in the assessment of avalanche danger is required. Areas with glide cracks are to be avoided as far as possible.
Snowpack
dp.6: cold, loose snow and wind
dp.3: rain
As a consequence of a moderate to strong northerly wind, clearly visible wind slabs formed especially adjacent to ridgelines. This also applies in gullies and bowls below the tree line. Over a wide area new snow and wind slabs are lying on the smooth surface of an old snowpack, especially above approximately 1900 m.
The old snowpack is moist, in particular at low and intermediate altitudes. Faceted weak layers exist in the centre of the snowpack in particular above the tree line.
Tendency
Fresh wind slabs are to be evaluated with care and prudence.













