Danger level
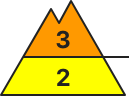 | 2400m |
|  |
|  | ||||
|  |
|  |

Weakly bonded old snow requires caution. Fresh wind slabs are to be evaluated with care and prudence.
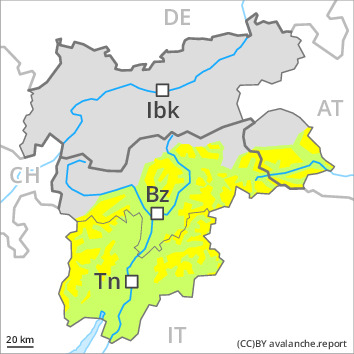
Weak layers in the old snowpack can still be released by individual winter sport participants. Caution is to be exercised in particular on steep shady slopes above approximately 2400 m, as well as on steep sunny slopes in high Alpine regions. In particular transitions from a shallow to a deep snowpack are especially unfavourable. Remotely triggered avalanches are possible in isolated cases. In isolated cases avalanches are large. Whumpfing sounds and the formation of shooting cracks when stepping on the snowpack indicate poor snowpack stability. The avalanche prone locations are but are barely recognisable, even to the trained eye. Defensive route selection is appropriate.
The fresh wind slabs are in some cases prone to triggering, in particular on steep shady slopes above the tree line, as well as in all aspects at elevated altitudes.
On very steep sunny slopes wet and gliding avalanches are possible as the day progresses.
Snowpack
dp.6: cold, loose snow and wind
dp.1: deep persistent weak layer
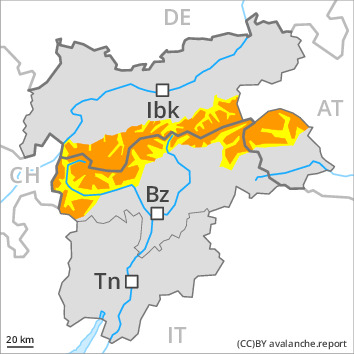
Distinct weak layers in the old snowpack confirm the complex avalanche situation on steep shady slopes. In its middle, the snowpack is faceted and weak, in particular on shady slopes above approximately 2400 m, as well as on sunny slopes at elevated altitudes.
The fresh wind slabs will be deposited on the unfavourable surface of an old snowpack in particular on steep shady slopes at high altitudes and in high Alpine regions. As a consequence of mild temperatures and solar radiation the snowpack will consolidate.
Sunshine and high temperatures will give rise as the day progresses to slight moistening of the snowpack. As a consequence of mild temperatures a crust formed on the surface during the last few days.
Tendency
Weakly bonded old snow is to be avoided.