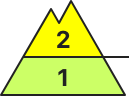
Danger level
 | 2400m |
|  |
| 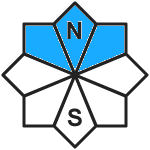 |

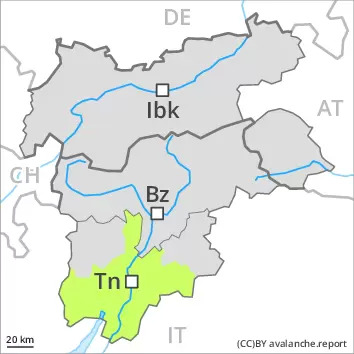
The snowpack will be in most cases stable. Wind slabs require caution.
As a consequence of a strong northerly wind, sometimes avalanche prone wind slabs formed in some localities. These avalanche prone locations are to be found in particular on very steep shady slopes at elevated altitudes and in gullies and bowls, and behind abrupt changes in the terrain. They are mostly easy to recognise. Weak layers in the old snowpack can be released in isolated cases and mostly by large additional loads on steep shady slopes. At lower altitudes and below the tree line hardly any snow is lying.
Snowpack
At high altitudes and in high Alpine regions less snow than usual is lying. As a consequence of solar radiation the snow drift accumulations stabilised during the last few days, in particular on sunny slopes. Here the snowpack is better bonded.
The old snowpack will be prone to triggering in some places, especially on shady slopes above approximately 2400 m.
Tendency
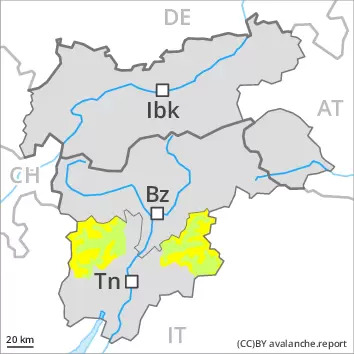
The avalanche danger will persist.